8 Commission Structure Examples to Maximize Sales in 2025
Finding the right way to pay your partners or sales team is crucial for driving growth and motivating performance. A well-designed commission plan can ignite sales, while a poorly structured one can lead to confusion and missed targets. This guide is built to give you clarity by breaking down eight essential commission structure examples you can implement today.
We will move beyond basic definitions and dive deep into the mechanics of each model. For every structure, you'll find a detailed analysis, concrete examples often tied to an Amazon sales context, and a clear breakdown of the pros and cons. We'll explore who each model is best for, from Amazon brands building their first affiliate program to sales managers refining compensation plans for a growing team.
This article provides the strategic insights you need to choose and apply the right framework. Whether you're a brand owner, a content creator, or a sales leader, understanding these payout models is a powerful advantage. Let's explore the structures that transform effort into exceptional results.
1. Straight Commission Structure
The Straight Commission structure is one of the most direct and performance-driven commission structure examples. In this model, compensation is based entirely on sales performance. A sales representative earns a fixed percentage of the revenue they generate, with no base salary or hourly wage. This 100% commission model directly links earnings to results, creating a powerful incentive for high performance.

This model is popular in industries with high-ticket items and clear sales cycles, such as real estate and automotive sales. The direct correlation between effort and reward attracts highly motivated, entrepreneurial individuals who are confident in their ability to sell. For businesses, this structure minimizes fixed labor costs and financial risk, as compensation is only paid out upon successful sales.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure is a powerful motivator. Since earnings are uncapped, top performers have unlimited potential, driving them to exceed sales targets consistently.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For the company, this is a low-risk model. You avoid paying salaries to underperforming representatives, making your sales costs variable and directly tied to revenue.
- Attraction & Retention: It attracts confident, risk-tolerant "hunter" personality types. However, it can lead to high turnover, especially among new hires who struggle to build a sales pipeline quickly.
Best-Practice Application
Consider using a straight commission model when your product has a high-profit margin and a relatively short sales cycle. This ensures that representatives can earn a substantial income in a reasonable timeframe.
Key Insight: To mitigate the high turnover risk associated with straight commission, many companies offer a "draw against commission." This is a pre-determined advance payment that the salesperson must pay back from their future commissions, providing a safety net during the initial ramp-up period.
For Amazon sellers or brands working with affiliates, this model is less common. However, the principle applies to performance-based marketing where affiliates are only paid a percentage of the sales they drive, with no upfront fees. This pure pay-for-performance approach ensures your marketing spend directly generates revenue.
2. Base Plus Commission Structure
The Base Plus Commission structure is a hybrid compensation model that combines the stability of a fixed base salary with the motivation of performance-based commissions. This balanced approach is one of the most widely adopted commission structure examples, as it provides sales representatives with a predictable income while still incentivizing them to drive sales. Employees receive a regular salary, supplemented by a percentage of the revenue they generate.
This model is extremely popular in industries like B2B software sales, technology, and pharmaceuticals, where sales cycles can be long and complex. It offers a crucial safety net that helps attract and retain a wider range of talent, not just high-risk "hunters." For businesses, this structure fosters loyalty and encourages representatives to focus on long-term relationship-building rather than just quick, high-volume sales.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: The commission component keeps representatives hungry and focused on hitting targets, while the base salary reduces the anxiety associated with income volatility. This balance promotes consistent, sustainable performance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While it carries higher fixed costs than a straight commission model, the base salary is typically lower than a standard salaried role. The variable commission ensures that a significant portion of labor costs is still directly tied to revenue.
- Attraction & Retention: This structure appeals to a broader talent pool, including experienced professionals who require income stability. It significantly reduces turnover compared to commission-only roles, saving the company on recruitment and training costs.
Best-Practice Application
Implement a base plus commission model when your sales cycle is longer, or when non-sales activities like customer nurturing and education are critical. A common practice is to set the base salary to constitute 60-80% of the total target compensation, with commission making up the remaining 20-40%.
Key Insight: To optimize this structure, ensure your commission thresholds are realistic and achievable. Setting unattainable goals can demotivate the sales team and negate the benefits of the incentive, making the commission feel like an empty promise rather than a real performance driver.
For Amazon brands building an internal sales team to handle B2B or wholesale accounts, this model is ideal. It provides the security needed to attract skilled professionals who can manage complex relationships and drive large-volume orders, ultimately scaling your brand beyond the direct-to-consumer marketplace.
3. Tiered Commission Structure
The Tiered Commission Structure is a progressive system designed to reward high achievement. In this model, the commission rate increases as a sales representative surpasses pre-defined sales targets or revenue thresholds. This approach provides a powerful, escalating incentive for sales reps to not only meet but significantly exceed their quotas.
The bar chart below clearly illustrates how earnings accelerate as sales volume grows within a typical tiered framework.
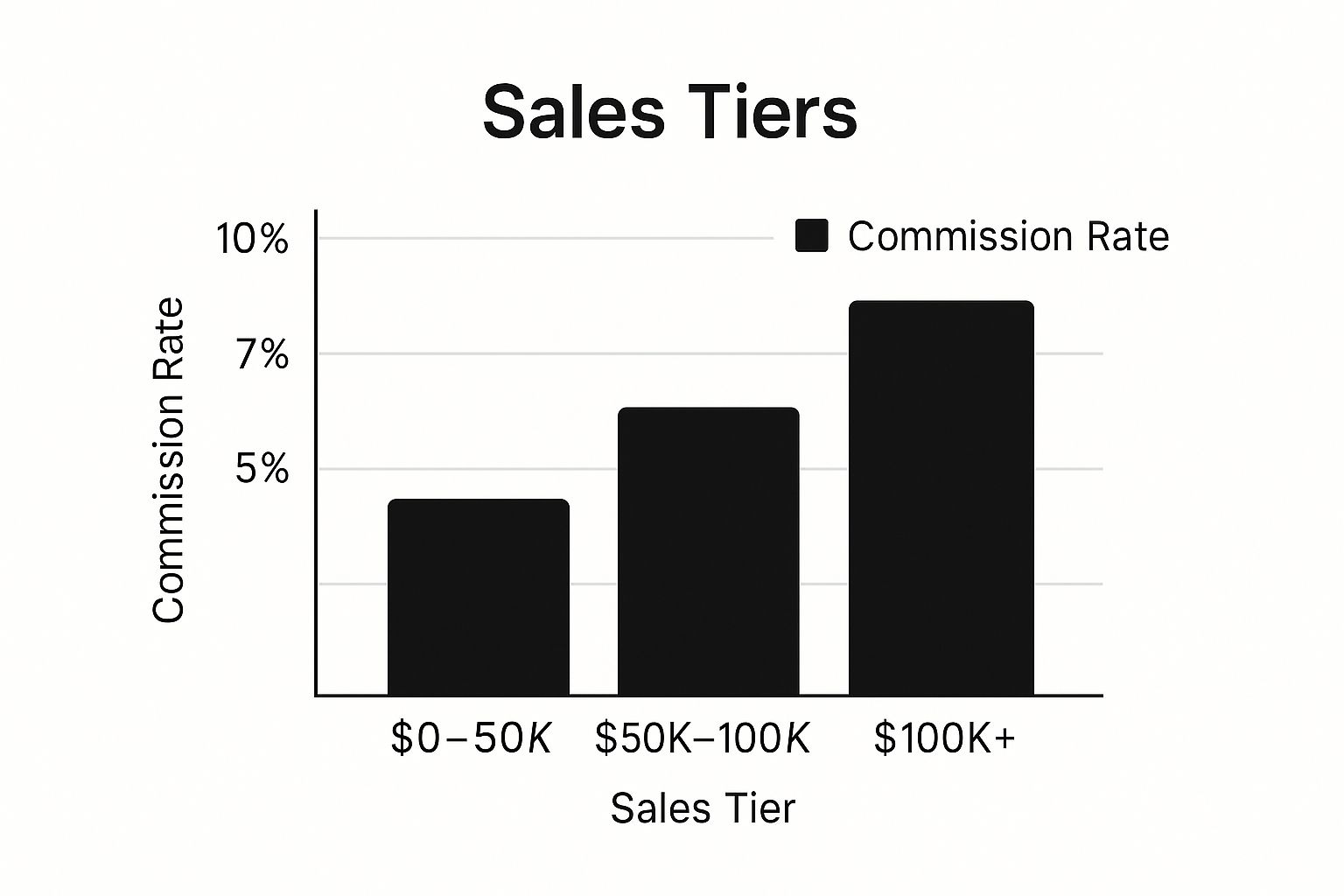
This visualization shows the significant jump in earning potential from 5% to 10% as a salesperson moves from the entry-level tier to the top performance bracket. Popularized by enterprise software companies and luxury real estate firms, this structure is ideal for environments with scalable sales potential, motivating the entire team to reach higher levels of performance.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure creates "superstar" motivation. The prospect of a higher commission rate for the next sale is a powerful short-term driver that keeps top performers engaged and pushing past their goals.
- Performance Segmentation: It naturally segments your sales team. You can easily identify your top, mid-level, and entry-level performers, allowing for targeted training and support.
- Sales Growth: By incentivizing higher volume, it directly fuels overall revenue growth. It encourages reps to close one more deal before the end of a period to reach the next, more lucrative tier.
Best-Practice Application
Use a tiered commission model when you want to aggressively grow sales volume and strongly reward your top producers. Ensure the tiers are realistic and achievable, yet challenging enough to motivate extra effort.
Key Insight: To maximize effectiveness, keep the number of tiers limited to three or four. Too many levels can become confusing and dilute the motivational impact of reaching the next threshold. Provide reps with a real-time dashboard to track their progress toward the next tier.
For Amazon sellers using an affiliate program, a tiered structure can be highly effective. You can offer a base commission rate to all affiliates and then create higher tiers for those who drive a certain volume of sales or revenue per month. This encourages your best partners to promote your products even more heavily.
4. Revenue Commission Structure
The Revenue Commission Structure is one of the most widely used commission structure examples, tying compensation directly to top-line sales. In this model, a sales representative earns a predetermined percentage of the total revenue they generate from a sale. Unlike profit-based models, this structure focuses on the gross sales amount, making calculations simple and transparent.
This approach is prevalent in industries where market share and sales volume are key performance indicators, such as traditional retail, technology (SaaS), and wholesale distribution. By rewarding top-line growth, it encourages sales teams to focus on generating as much revenue as possible. For businesses, it provides a clear and predictable way to calculate sales costs as a percentage of overall revenue.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure strongly incentivizes high-volume sales. Representatives are motivated to close larger deals and increase order values, as their earnings are directly proportional to the total revenue they bring in.
- Simplicity: It's easy for both the company and the salesperson to understand and calculate. This transparency reduces disputes over commission payouts and simplifies financial forecasting.
- Market Penetration: Focusing on revenue is an effective strategy for companies trying to gain market share or establish a strong presence. It pushes the sales team to prioritize customer acquisition and sales volume above all else.
Best-Practice Application
Implement a revenue commission model when your primary goal is rapid growth and market expansion. It's particularly effective for products with consistent profit margins, where higher revenue reliably translates to higher profit.
Key Insight: To protect profitability, businesses often pair a revenue commission structure with minimum margin requirements or clawback clauses. This prevents sales reps from offering excessive discounts just to close a deal, ensuring that sales remain profitable for the company.
For Amazon sellers, this model aligns perfectly with many ecommerce affiliate marketing programs where affiliates earn a percentage of the total sale price. This simplicity encourages creators and influencers to promote products, as their potential earnings are clear from the outset. You can learn more about how to set up these programs and explore different commission structures for ecommerce brands to drive more traffic and sales.
5. Gross Margin Commission Structure
The Gross Margin Commission structure shifts the focus from pure revenue to profitability. Instead of earning a percentage of the total sale price, a representative earns a percentage of the gross profit margin. This model directly aligns the sales team's incentives with the company's financial health, encouraging them to sell based on value rather than just volume or price.
This approach is one of the most strategically sound commission structure examples for businesses with variable product costs or those that empower sales reps to negotiate discounts. It's prevalent in manufacturing, custom B2B solutions, and consulting services, where protecting profitability on each deal is critical. It prevents the common issue of salespeople heavily discounting products just to close deals and hit revenue targets, which can erode company profits.
Strategic Breakdown
- Profitability Focus: This structure incentivizes value-based selling. Representatives are motivated to protect pricing and avoid unnecessary discounts because their commission is directly tied to the profit of the deal, not just the top-line revenue.
- Salesperson Empowerment: It gives salespeople a clear understanding of how their decisions impact the bottom line. This fosters a sense of business ownership and encourages smarter, more strategic deal-making.
- Complexity & Transparency: The primary challenge is complexity. The company must provide clear, transparent data on the cost of goods sold (COGS) for each product so reps can accurately calculate their potential earnings.
Best-Practice Application
Implement this model when your sales team has the authority to negotiate pricing. It's ideal for businesses selling custom products or technology solutions where margins can vary significantly from one deal to the next.
Key Insight: To make this model effective, provide your sales team with simple tools, like a margin calculator, to quickly see how discounts affect their commission. Set clear minimum margin thresholds for deals to prevent unprofitable sales and ensure every transaction contributes positively to the bottom line.
For Amazon sellers using an affiliate or influencer network, this concept can be adapted. While you can't share COGS data, you can create tiered commission rates that reward affiliates for promoting higher-margin products. This steers your promotional traffic toward your most profitable items, aligning their efforts with your business goals without revealing sensitive cost information.
6. Territory Volume Bonus Structure
The Territory Volume Bonus structure incentivizes sales representatives based on the collective performance of an assigned geographic area or market segment. While individual commissions may still exist, this model adds a layer of compensation tied to the overall sales volume or growth within the entire territory. This approach fosters collaboration, long-term market development, and a focus on broad customer penetration rather than just individual wins.
This model is common in industries where teamwork and market health are crucial, such as pharmaceuticals, B2B equipment sales, and food distribution. It encourages reps to support each other, share leads, and work towards a common goal, preventing internal competition that could harm customer relationships or brand reputation within a region.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure motivates reps to think bigger than their own sales quota. They become invested in the long-term health and growth of their territory, leading to better customer service and market saturation.
- Team Collaboration: By tying a portion of earnings to group success, it encourages a team-oriented sales culture. Senior reps are more likely to mentor junior reps, knowing that everyone’s success contributes to their bonus.
- Market Development: It's ideal for companies looking to expand their footprint. Reps are rewarded for developing new accounts and increasing market share across the region, not just closing the easiest deals.
Best-Practice Application
Use a Territory Volume Bonus structure when your sales cycle is long and requires a coordinated team effort. Clearly define territory boundaries and set realistic, achievable growth targets based on market maturity and potential.
Key Insight: To maintain individual accountability, it's crucial to balance territory bonuses with individual performance metrics. A hybrid model, where 70% of commission comes from individual sales and 30% from the territory bonus, often strikes the right balance between personal drive and team collaboration.
For Amazon sellers expanding into new regions or countries, this principle can be applied to affiliate teams. A team of affiliates targeting a specific country, like Germany or Japan, could receive a bonus based on the total sales volume they generate collectively for that marketplace, encouraging them to share successful strategies and support each other's growth.
7. Draw Against Commission Structure
The Draw Against Commission structure is a hybrid model designed to offer sales representatives the stability of a regular paycheck while retaining a strong performance-based incentive. In this system, a representative receives a predetermined advance payment, or "draw," at regular intervals. This draw is then paid back from the commissions they earn, effectively acting as a loan against future earnings.
This model bridges the gap between a salaried position and a straight commission role, making it ideal for industries with long or unpredictable sales cycles, such as high-end real estate or enterprise insurance. It provides new hires with a financial cushion as they build their sales pipeline. For the business, it helps attract talented individuals who may be too risk-averse for a 100% commission job, while still tying compensation directly to sales results over the long term.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure maintains high motivation by keeping commission as the primary driver of total earnings. The draw provides security, allowing reps to focus on closing larger, more complex deals without immediate financial stress.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While there's an upfront cost, the draw is typically "recoverable," meaning the company recoups the advance from earned commissions. This mitigates the financial risk compared to a fixed salary if a representative underperforms.
- Attraction & Retention: This model widens the talent pool by appealing to skilled salespeople who require income stability. It can significantly reduce the high turnover often seen in pure commission roles, especially during an employee's first few months.
Best-Practice Application
Use a draw against commission model when onboarding new team members or when your sales cycle is longer than a standard pay period. It provides the necessary runway for reps to succeed.
Key Insight: To make this model effective, set clear and fair terms for draw recovery. The draw should be substantial enough to cover basic living expenses but not so high that it becomes difficult to pay back, which could demotivate the representative. Setting the draw at 50-70% of expected on-target earnings is a common best practice.
For brands using performance marketing, this concept is less direct but relates to providing partners with initial resources or retainers that are later reconciled against performance targets. Proper setup and tracking are crucial, just as with other compensation models, and a robust affiliate program management strategy ensures all payments are handled correctly.
8. Team-Based Commission Structure
The Team-Based Commission structure shifts the focus from individual achievement to collective success. In this model, compensation is tied to the performance of an entire team or group rather than the results of a single representative. This collaborative approach encourages teamwork, knowledge sharing, and a unified effort toward common goals.
This model is increasingly popular in complex sales environments like technology and consulting, where multiple touchpoints and roles contribute to closing a deal. For instance, a sales pod might include a sales development rep, an account executive, and a solutions engineer, all sharing in the commission from a successful sale. This structure fosters a supportive environment where members are motivated to help each other succeed.
Strategic Breakdown
- Motivation: This structure incentivizes collaboration and mutual support. It discourages internal competition and encourages senior members to mentor junior colleagues, strengthening the entire team.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It can simplify commission calculations and administration. By pooling commissions, the company ensures that key support roles, which are crucial but do not directly close deals, are rewarded for their contributions.
- Attraction & Retention: It appeals to collaborative individuals who thrive in a team setting. This can reduce the "lone wolf" mentality and create a more stable, less cutthroat sales culture, potentially lowering turnover.
Best-Practice Application
Implement a team-based commission structure when your sales process is long, complex, and requires collaboration across multiple roles. Clear, measurable team goals are essential for success.
Key Insight: To maintain individual accountability, consider a hybrid model. A portion of the commission could be based on team performance, while the remainder is tied to individual metrics. This balances collaborative goals with personal motivation and recognizes top performers.
For Amazon brands, this can be applied to your affiliate or influencer marketing teams. Instead of just paying an individual creator, you could offer a team bonus if a group of creators collaborating on a campaign achieves a collective sales target. This approach is powerful for turning individual creators into a network of true brand advocates working together.
Comparison of 8 Commission Structures
| Commission Structure | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | 🛠️ Resource Requirements | 📊 Expected Outcomes | 💡 Ideal Use Cases | ⭐ Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straight Commission Structure | Low 🔄 | Low (no base salary) | High earning volatility, strong motivation | High-risk sales roles (e.g., real estate) | Unlimited earnings, simple to calculate ⭐ |
| Base Plus Commission Structure | Moderate 🔄 | Moderate (base + commission payroll) | Income stability with performance incentives | SaaS, pharmaceuticals, retail | Balances risk & reward, attracts talent ⭐ |
| Tiered Commission Structure | High 🔄 | Moderate to High | Motivates sustained excellence | Enterprise software, luxury sales | Rewards overachievement, clear goals ⭐ |
| Revenue Commission Structure | Low 🔄 | Low | Focus on volume growth | Retail, automotive, wholesale | Simple, quick commission, transparent ⭐ |
| Gross Margin Commission Structure | High 🔄 | High (cost data & accounting) | Aligns sales with profitability | Manufacturing, consulting, B2B services | Promotes profitable sales, margin focus ⭐ |
| Territory Volume Bonus Structure | Moderate 🔄 | Moderate | Encourages regional growth | Pharma, industrial equipment, food service | Rewards territory development ⭐ |
| Draw Against Commission Structure | High 🔄 | High (advance payments & recovery) | Income stability with commission motivation | Real estate, insurance, automotive | Smooths cash flow, attracts talent ⭐ |
| Team-Based Commission Structure | High 🔄 | High (team coordination) | Promotes collaboration and team success | Tech, consulting, customer success | Builds teamwork, reduces internal conflict ⭐ |
Implementing Your Perfect Commission Structure
Choosing the right commission structure is not about finding a single "best" option. As we've explored through various commission structure examples, the ideal model is a strategic decision that aligns directly with your brand’s specific goals, sales cycle, and the nature of your affiliate partnerships. Whether you’re incentivizing high-volume sales with a tiered system or protecting profit margins with a gross margin model, your choice sets the foundation for a successful affiliate program.
The key takeaway is that no structure operates in a vacuum. The most effective programs are dynamic, transparent, and supported by robust technology. For Amazon sellers, this means moving beyond a one-size-fits-all approach and embracing flexibility.
From Theory to Actionable Strategy
Transitioning from understanding these models to implementing them requires a clear plan. Here are the essential steps to put what you’ve learned into practice:
- Define Your Primary Goal: Are you focused on rapid market penetration, maximizing profitability per sale, or encouraging team collaboration? Your answer will immediately narrow down the most suitable commission structures. For example, a goal of aggressive growth might favor a Straight or Tiered Commission model.
- Communicate with Absolute Clarity: Ambiguity is the enemy of motivation. Your affiliates must understand exactly how they earn, what the performance benchmarks are, and when they get paid. Create a simple, clear document outlining the commission rules and make it easily accessible.
- Track Everything Meticulously: Trust is built on accurate and transparent tracking. Leveraging tools like Amazon Attribution is non-negotiable for crediting sales correctly. To effectively monitor the success of your chosen structure, it's vital to create a KPI dashboard that visualizes key metrics like conversion rates, affiliate performance, and overall ROI.
The Power of a Hybrid Approach
Remember that you don't have to be rigid. The most sophisticated affiliate programs often blend elements from different commission structure examples. You might offer a stable Base Plus Commission for new creators to help them get started, while reserving a high-reward Tiered structure for your top-performing partners. This hybrid approach allows you to cater to different affiliate levels, keeping your entire network motivated and engaged.
Ultimately, the right commission structure is a powerful lever for growth. It’s more than just a payment plan; it’s a strategic tool that aligns your brand’s objectives with the ambitions of your partners. By selecting a model that fits your business and empowering it with transparent processes and the right technology, you can build a resilient, scalable, and highly profitable affiliate network that drives consistent results on Amazon and beyond.
Ready to implement these advanced commission strategies without the manual hassle? Coral provides the tools you need to create custom, flexible commission plans for each of your Amazon affiliates. Manage tiered rates, track performance with precision, and automate payouts to build a motivated and loyal creator network. Learn how Coral can transform your affiliate program today.